Citrus x Sinensis sweet orange, also known as the sweet orange. Discover its uses, benefits, and why it’s a must-have in your diet. Perfect for readers!
Citrus × sinensis
A hybrid citrus species known as sweet oranges
| Hybrid composition | A hybrid between pomelo (Citrus maxima) and mandarin (Citrus reticulata) |
| Main varieties | Includes Valencia oranges, blood oranges, and navel oranges |
| Uses | Used for the juicy fruit pulp, aromatic peel (rind), orange blossoms, leaves, and wood |
Introduction: Citrus × Sinensis Sweet Orange
Welcome to the vibrant and zesty world of Citrus × Sinensis, a fruit that not only tantalizes your taste buds but also brings a bounty of health benefits to your table. Commonly known as the sweet orange, this citrus marvel is a staple in diets around the globe, revered not just for its delicious flavor but for its nutritional and medicinal properties as well. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about Citrus × Sinensis, from its uses and common names to its impact on health and beauty. So, let’s peel back the layers and discover the juicy secrets of the sweet orange!
What is Citrus × Sinensis Used For?
Culinary Delights
Citrus × Sinensis is a versatile fruit that finds its way into a myriad of culinary creations. From the refreshing tang of orange juice to the zest that brightens up cakes and salads, the sweet orange is a kitchen favorite.
Medicinal Uses
Rich in vitamin C and antioxidants, Citrus × Sinensis is used to bolster the immune system, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and even lower blood pressure.
What is Citrus × Sinensis Called?
Citrus × Sinensis is known by several names, including sweet orange, navel orange, and Valencia orange, each variant bringing its own unique flavor and characteristics to the table.
What are Common Names for Citrus × Sinensis?
Apart from its scientific moniker, Citrus × Sinensis is commonly referred to as the sweet orange. Depending on the variety, it may also be called navel orange, blood orange, or Cara Cara orange.
Can You Eat Citrus × Sinensis?
Absolutely! Every part of Citrus × Sinensis, from its juicy flesh to its aromatic zest, is edible. The fruit can be consumed fresh, juiced, or used as a flavor enhancer in both sweet and savory dishes.
What is Citrus Good For?
Citrus fruits, including Citrus × Sinensis, are good for much more than just their taste. They’re packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support heart health, skin health, and immune function.
Is Citrus × Sinensis Good for Hair?
Yes, the high vitamin C content in Citrus × Sinensis promotes collagen production, which is essential for healthy hair growth. Its antioxidants can also protect hair from environmental damage.
What are the 4 Types of Citrus?
The four main types of citrus fruits are oranges (including Citrus × Sinensis), lemons, limes, and grapefruits. Each type offers its own unique set of flavors and health benefits.
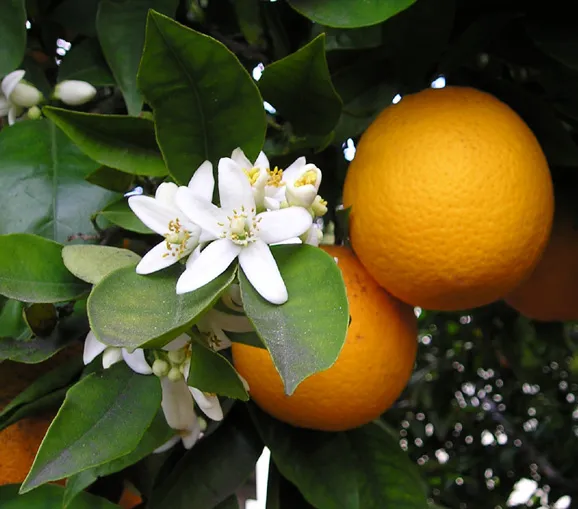

What is Called Citrus Fruit?
A citrus fruit is any fruit belonging to the genus Citrus, characterized by their juicy segments, tangy flavor, and high vitamin C content. This includes oranges, lemons, limes, and grapefruits.
Why is it Called Citrus?
The term “citrus” is derived from the Latin word “citrus,” which referred to the citron tree. The name has since expanded to encompass all fruits within the Citrus genus, known for their sour to sweet flavors.
Is Citrus × Sinensis a Dry or Fleshy Fruit?
Citrus × Sinensis is considered a fleshy fruit. Specifically, it’s classified as a hesperidium, a type of berry with a leathery rind and juicy segments.
What are the Nutrients in Citrus × Sinensis?
Citrus × Sinensis is rich in vitamin C, flavonoids, and carotenoids. It also contains fiber, potassium, and several B vitamins, making it a nutrient-dense choice for a healthy diet.
What is the Flower of Citrus × Sinensis?
The flower of Citrus × Sinensis is known as the orange blossom. It’s highly fragrant, white, and often used in perfumery, culinary creations, and traditional ceremonies.
what are the different types of citrus sinensis?
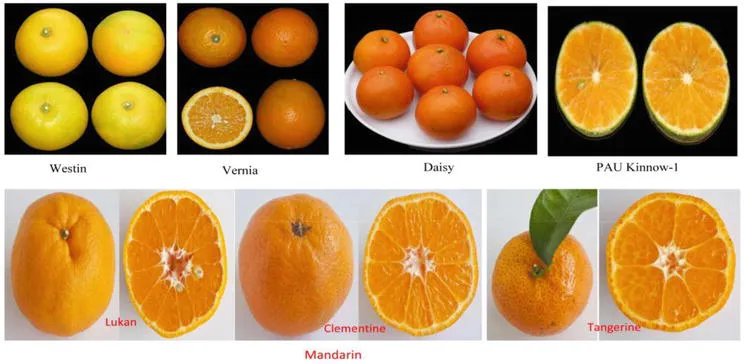
The different types of Citrus sinensis, commonly known as sweet orange, include a variety of cultivars and hybrids, each with unique characteristics, flavors, and ripening times. Here are some of the types mentioned across the sources:
- Navel Oranges: These are characterized by the growth of a second fruit at the apex, which protrudes slightly and resembles a human navel. Navel oranges are seedless, easy to peel, and are considered one of the world’s best-tasting oranges due to their sweet and juicy nature.
- Blood Oranges: Known for their distinctive dark red flesh, blood oranges have a unique flavor compared to other orange varieties, often described as being slightly raspberry-like in addition to the usual citrus notes. The color is due to the presence of anthocyanins, a family of antioxidant pigments common to many flowers and fruit, but uncommon in citrus fruits.
- Valencia Oranges: Often associated with orange juice, Valencia oranges have thin skins and are very juicy. They are excellent for both eating and juicing. This variety is prized for its sweetness and a perfect balance of tartness.
- Cara Cara Oranges: A type of navel orange, Cara Cara oranges have a distinctive pinkish-red flesh instead of the traditional orange color. They offer a sweet taste with hints of berry.
- Washington Navel: A specific type of navel orange, the Washington Navel is noted for its large size, sweetness, and seedless interior. It ripens in January-February and is very sweet and juicy.
- Moro: Identified as a type of blood orange, Moro oranges are known for their deep red flesh and a flavor that blends the sweetness of the orange with a hint of raspberry.
- Common Oranges: This class includes the typical sweet oranges that are widely consumed around the world. They are valued for their sweet flavor and versatility.
- Acidless Oranges: Also known as “sweet” oranges, these have very low levels of acid, making them less tangy than other varieties. They are not widely available and are more common in the Mediterranean region.
Each of these types of Citrus sinensis offers unique flavors and characteristics, making them suitable for a variety of culinary uses, from fresh consumption to juice production and culinary enhancements.
What are the health benefits of citrus sinensis?
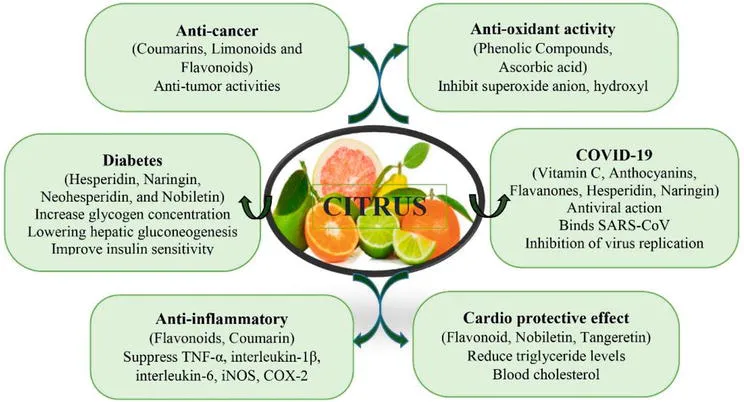
Citrus sinensis, commonly known as sweet orange, offers a wide range of health benefits primarily due to its rich content of vitamins, minerals, and bioactive compounds. Here are the key health benefits based on the provided sources:
- Boosts Immune System: Citrus sinensis is an excellent source of vitamin C, which is crucial for the proper function of the immune system. Vitamin C helps stimulate the production of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting infections.
- Promotes Heart Health: The fruit contains flavonoids like hesperidin, which have been shown to lower cholesterol levels and prevent the arteries from getting clogged. This can reduce the risk of heart disease. Additionally, the potassium content in oranges helps lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of stroke.
- Antioxidant Properties: Citrus sinensis is loaded with antioxidants, including vitamin C, flavonoids, and carotenoids, which help protect the body against free radicals. Antioxidants play a role in reducing oxidative stress and can help prevent chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
- Skin Health: The high levels of vitamin C in sweet orange aid in the production of collagen, which is important for maintaining skin elasticity and preventing premature aging. Vitamin C also helps repair damaged skin cells, promoting a healthier complexion.
- Prevents Kidney Stones: The citrate content in sweet orange helps prevent kidney stone formation by binding with calcium in the urine, which might otherwise crystallize and form stones.
- Supports Digestive Health: Citrus sinensis is high in dietary fiber, which is beneficial for digestive health. Fiber helps regulate bowel movements and can prevent digestive disorders like constipation and ulcers.
- Eye Health: The fruit is rich in vitamin A and other antioxidants like beta-carotene, which are essential for maintaining healthy vision. These nutrients help protect the eyes from age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: The flavonoids in Citrus sinensis also exhibit anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation in the body, potentially benefiting conditions like arthritis and asthma.
- Cancer Prevention: Some studies suggest that the compounds in Citrus sinensis, such as limonoids and flavonoids, may have anti-cancer properties. These compounds can help inhibit tumor growth and promote cancer cell death.
- Mental Health Benefits: The folate and folic acid found in Citrus sinensis contribute to brain health and development. These nutrients can help prevent neurological disorders and improve overall brain function.
In summary, Citrus sinensis is a nutrient-rich fruit that offers a multitude of health benefits, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet. Its components not only support physical health but also contribute to mental well-being.
How is citrus x sinensis sweet orange used in traditional medicine?
Citrus x Sinensis sweet orange, commonly known as sweet orange, has been used in traditional medicine across various cultures to treat a wide array of ailments. The uses in traditional medicine, as highlighted by the sources, include:
- Digestive Health: It has been traditionally used to treat constipation, cramps, colic, and diarrhea. The fruit is known for its fiber content, which can aid in digestion and promote regular bowel movements.
- Respiratory Conditions: Citrus sinensis has been used to treat bronchitis, tuberculosis, cough, and cold. Its vitamin C content and other phytochemicals may help in relieving respiratory conditions and boosting the immune system.
- Metabolic and Cardiovascular Health: Traditional uses also include the treatment of obesity, menstrual disorders, angina, and hypertension. These conditions are related to the metabolic and cardiovascular systems, and the fruit’s bioactive compounds may have beneficial effects.
- Neurological and Mental Health: It has been used to manage anxiety, depression, and stress. The calming effect of Citrus sinensis, possibly due to its aromatic compounds, may contribute to its use in mental and neurological health.
- Other Conditions: Additional traditional uses include the management of arthritis, asthma, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, macular degeneration, diabetes mellitus, gallstones, multiple sclerosis, cholera, gingivitis, cataracts, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn’s disease. These wide-ranging applications highlight the fruit’s versatility in traditional medicine practices1.
- General Health and Well-being: Citrus sinensis is used as a general tonic and to maintain hydration. Its juice is particularly noted for this purpose. In Mexican traditional medicine, it is used for the treatment of tuberculosis, and in France, it is utilized for angina, constipation, menstrual disorders, and hypertension. In Chinese medicine, the orange is valued as a cooling agent for coughs, colds, and respiratory disorders1.
- Magic/Ritual Significance: Beyond its medicinal uses, Citrus sinensis is also noted for its magic and ritual significance. It is believed that the high-energy scent of Citrus sinensis communicates the joy of angels to human beings and embodies the sun in various mixtures, whether potpourri, tea, sachet, or charm, making it a symbol of good luck in China1.
These traditional uses are supported by the presence of various phytochemicals in Citrus sinensis, including vitamins (especially vitamin C), synephrine, limonoids, hesperidin flavonoid, polyphenols, and pectin, which contribute to its health-promoting properties.
Conclusion: Citrus x Sinensis sweet orange
Citrus x Sinensis sweet orange, or the sweet orange, is more than just a delicious fruit. It’s a powerhouse of nutrients and antioxidants that can enhance your health in numerous ways. Whether you’re enjoying a glass of fresh orange juice or zesting up your favorite dish, incorporating Citrus × Sinensis into your diet is a tasty way to boost your overall well-being. So, the next time you pass by these orange gems at the grocery store, remember the myriad of benefits they hold within their juicy embrace.

What i do not understood is in truth how you are not actually a lot more smartlyliked than you may be now You are very intelligent You realize therefore significantly in the case of this topic produced me individually imagine it from numerous numerous angles Its like men and women dont seem to be fascinated until it is one thing to do with Woman gaga Your own stuffs nice All the time care for it up
helloI really like your writing so a lot share we keep up a correspondence extra approximately your post on AOL I need an expert in this house to unravel my problem May be that is you Taking a look ahead to see you
Excellent blog here Also your website loads up very fast What web host are you using Can I get your affiliate link to your host I wish my web site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
I applaud your devotion. I’ve looked at your sketch, and the material you’ve created is excellent. Nevertheless, you appear to be apprehensive about the prospect of heading in a direction that could cause discomfort. I agree with you that you will be able to deal with this issue in a timely manner.
Eu concordo com todas as ideias que você introduziu em sua postagem. Elas são muito convincentes e com certeza funcionarão. Mesmo assim, as postagens são muito curtas para iniciantes. Você pode prolongá-las um pouco para as próximas vezes. Obrigado pela postagem.
Your blog is a breath of fresh air in the crowded online space. I appreciate the unique perspective you bring to every topic you cover. Keep up the fantastic work!
Wow superb blog layout How long have you been blogging for you make blogging look easy The overall look of your site is magnificent as well as the content
Alguém essencialmente ajudou a tornar os artigos significativos. Id state Esta é a primeira vez que visitei sua página da web e até agora me surpreendi com a pesquisa que você fez para tornar este post incrível Trabalho fantástico
Business dicker Good post! We will be linking to this particularly great post on our site. Keep up the great writing
startup talky Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites
obviously like your website but you need to test the spelling on quite a few of your posts Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very troublesome to inform the reality on the other hand Ill certainly come back again
Your blog is a true hidden gem on the internet. Your thoughtful analysis and engaging writing style set you apart from the crowd. Keep up the excellent work!
I’m really glad to hear that my article helped you feel hopeful!
Somebody essentially lend a hand to make significantly posts I might state That is the very first time I frequented your web page and up to now I surprised with the research you made to create this particular put up amazing Excellent job
I’m really glad to hear that my article helped you feel hopeful!
Wonderful web site Lots of useful info here Im sending it to a few friends ans additionally sharing in delicious And obviously thanks to your effort
I’m really glad to hear that my article helped you feel hopeful!
real estate shop I appreciate you sharing this blog post. Thanks Again. Cool.
I’m really glad to hear that my article helped you feel hopeful!