How plants grow ever wondered how a tiny seed becomes a giant tree? Discover the amazing process of plant growth, from roots to flowers!
Introduction: How Plants Grow
Welcome to the captivating world of plant growth! Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a curious observer, understanding how plants transform from tiny seeds into lush greenery is both fascinating and essential. This blog post will explore the various stages of plant growth, the scientific processes involved, and practical tips to ensure your plants thrive. Join us as we delve into the journey from seed to sprout and beyond, providing you with all the knowledge you need to foster a thriving garden.
The Stages of Plant Growth:
Seed Germination: The First Step
Before a plant can grow, its seed must germinate. Germination occurs when a seed’s conditions are just right, involving adequate moisture, the correct temperature, and often, the right amount of light. During germination, the seed absorbs water, swelling and breaking its outer shell. This activates enzymes that kickstart the growth process, leading to the development of the plant’s root, which anchors it into the soil, and a shoot that pushes towards the surface.
Seedling Development: Building the Foundation
Once the shoot reaches the surface, photosynthesis begins. This stage is crucial as the young plant, now a seedling, develops its first true leaves which are capable of photosynthesis. The seedling stage is sensitive; the young plant needs proper sunlight, water, and nutrients to build a strong foundation for future growth.
Understanding Photosynthesis:
The Powerhouse of Growth
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants use sunlight to synthesize nutrients from carbon dioxide and water. It involves the green pigment chlorophyll and generates oxygen as a byproduct. This process is not only crucial for the plant’s growth but also for the environment, as it contributes to the oxygen we breathe
Growth Factors Influencing Plant Health:
Light: The Essential Element
Plants require light to perform photosynthesis. The amount of light needed can vary significantly between different plant species. Some may thrive in full sunlight, while others prefer shaded environments. Understanding the specific light requirements of your plant is crucial for its health and productivity.
Water: Balancing Act
Just as with light, the amount of water a plant needs can vary widely. Overwatering can lead to root rot, while under-watering can stress the plant, stunting its growth. The key is to maintain a balance and ensure the soil is moist but not waterlogged.
Nutrients: The Building Blocks
Nutrients are vital for plant growth. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are the primary nutrients, each serving a specific purpose in plant development. Regularly testing your soil and using the appropriate fertilizers can promote healthy growth and vibrant blooms.
What are the different stages of plant growth?
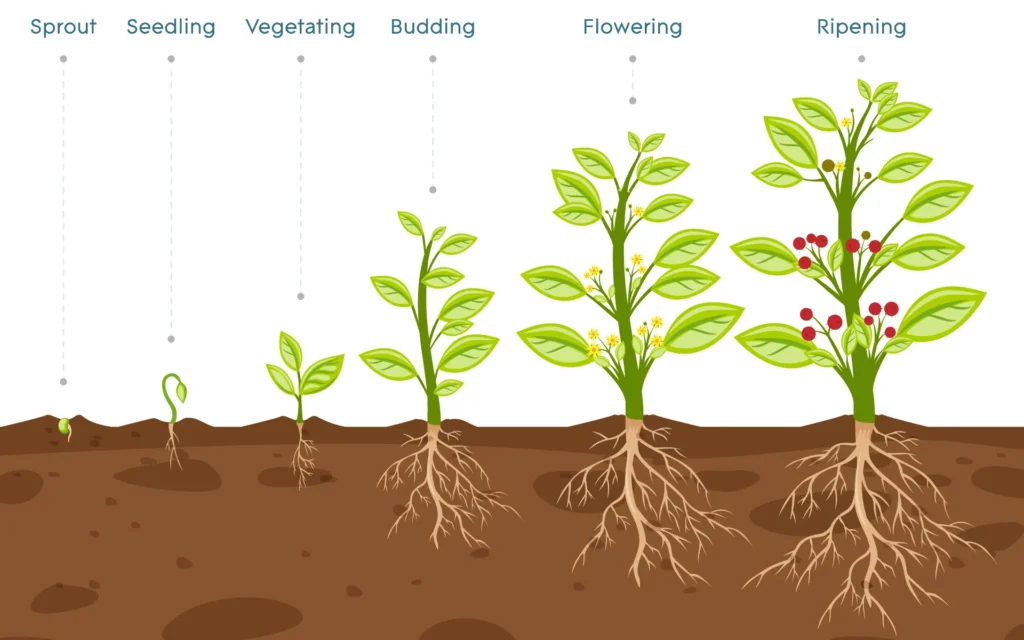
The different stages of how plants grow are generally categorized into several key phases, each critical for the development of a healthy plant. These stages include:
- Seed Germination: This is the initial stage where the seed begins to grow. It absorbs water, swells, and eventually breaks through its shell. The root begins to emerge, anchoring the plant into the soil, and a shoot pushes towards the surface.
- Seedling Development: After the shoot reaches the surface, the plant starts photosynthesis. This stage is crucial as the young plant develops its first true leaves, which are capable of photosynthesis. The plant is very sensitive during this phase and requires adequate sunlight, water, and nutrients.
- Vegetative Growth: During this stage, the plant’s root system and foliage expand. The plant primarily focuses on growing larger and stronger, producing more leaves and stems. This stage requires significant nutrients, particularly nitrogen, to support the rapid growth of foliage.
- Reproductive Stage: The plant begins to produce flowers and, subsequently, fruits and seeds. This stage marks a shift in the plant’s requirements, with an increased need for phosphorus and potassium to support flowering and fruit production. Some plants may require changes in light exposure to trigger this stage, especially in controlled environments like hydroponics.
- Pollination and Seed Production: Flowers are pollinated, leading to the production of seeds. This can occur through natural pollinators like bees and butterflies, or through manual methods in an indoor setting. This stage is crucial for the reproduction and spread of the plant species.
- Ripening and Seed Dispersal: After pollination, fruits ripen and seeds mature. The seeds are then dispersed through various means such as wind, water, or animals, which helps in the propagation of the plant species. This stage completes the life cycle of the plant, allowing it to spread and grow new individuals elsewhere.
These stages highlight the life cycle of a plant from a dormant seed to a mature individual capable of reproduction, emphasizing the different care and environmental conditions needed at each phase for optimal growth and development.
What are the factors that affect plant growth?
The growth and development of plants are influenced by a combination of factors, which can be broadly categorized into environmental, nutritional, and genetic factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing plant health and productivity, whether in natural ecosystems or agricultural settings.
Environmental Factors
- Light: Light is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. The intensity, quality, and duration of light affect plant growth. Too little light can lead to weak, spindly plants, while too much light can cause bleaching or burning of the leaves.
- Temperature: Temperature influences plant metabolic rates. Most plants have a specific temperature range for optimal growth. Extreme temperatures can inhibit plant growth, affect flowering and fruit set, and even cause plant death.
- Water: Water is crucial for plant life, affecting processes such as photosynthesis, nutrient transport, and cellular expansion. Both overwatering and underwatering can harm plant health, leading to issues like root rot or drought stress.
- Humidity: Humidity affects plant transpiration rates. High humidity can reduce water loss through transpiration, potentially leading to fungal diseases. Low humidity may increase transpiration to the point where the plant cannot replace lost water, leading to dehydration.
- Soil Quality: Soil structure, pH, and the presence of organic matter significantly impact plant growth. Soil quality influences water retention, aeration, and the availability of nutrients.
Nutritional Factors
- Macronutrients: Plants require several macronutrients in large amounts, including nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S). These nutrients are vital for various physiological functions, from growth and development to flowering and fruit production.
- Micronutrients: In addition to macronutrients, plants need micronutrients such as iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), boron (B), molybdenum (Mo), and chlorine (Cl) in smaller amounts. These elements play critical roles in enzymatic functions and plant defense mechanisms.
- Water and Nutrient Uptake: The ability of a plant to absorb water and nutrients from the soil is influenced by root system health and soil conditions. Optimal pH levels and soil structure facilitate the efficient uptake of water and essential nutrients.
Genetic Factors
- Intrinsic Growth Patterns: Each plant species and variety has genetically determined growth patterns, which dictate aspects such as size, shape, and the rate of development.
- Stress Resistance: Genetic factors also determine a plant’s resistance to environmental stresses, pests, and diseases. Some plants are bred for enhanced tolerance to specific conditions.
- Reproductive Strategies: The genetic makeup of a plant affects its flowering time, pollination mechanisms, and seed development, influencing overall reproductive success.
Conclusion: How Plants Grow
Understanding how plants grow is not just about keeping your garden green; it’s about appreciating the intricate processes that sustain life on Earth. By providing the right conditions for germination, ensuring adequate light for photosynthesis, and balancing water and nutrients, you can help your plants reach their full potential. Remember, each plant is unique, and learning about their specific needs will bring you closer to mastering the art of gardening.

Your work has captivated me just as much as it has captivated you. The visual display is elegant, and the written content is impressive. Nevertheless, you seem concerned about the possibility of delivering something that may be viewed as dubious. I agree that you’ll be able to address this issue promptly.
I was recommended this website by my cousin I am not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my trouble You are amazing Thanks
obviously like your website but you need to test the spelling on quite a few of your posts Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very troublesome to inform the reality on the other hand Ill certainly come back again
Fantastic beat I would like to apprentice while you amend your web site how could i subscribe for a blog site The account helped me a acceptable deal I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear concept
Your blog is a true hidden gem on the internet. Your thoughtful analysis and in-depth commentary set you apart from the crowd. Keep up the excellent work!
I was recommended this website by my cousin I am not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my difficulty You are wonderful Thanks
Wow amazing blog layout How long have you been blogging for you made blogging look easy The overall look of your web site is magnificent as well as the content
Hi my loved one I wish to say that this post is amazing nice written and include approximately all vital infos Id like to peer more posts like this
Obrigado, recentemente estive procurando informações sobre este assunto há algum tempo e a sua é a maior que descobri até agora. Mas e em relação aos resultados financeiros Você tem certeza em relação ao fornecimento
Meu irmão recomendou que eu pudesse gostar deste site Ele estava totalmente certo Este post realmente fez o meu dia Você não pode imaginar quanto tempo gastei com esta informação Obrigado
Program iz Great information shared.. really enjoyed reading this post thank you author for sharing this post .. appreciated
I’m really glad to hear that my article helped you feel hopeful!
Techno rozen I just like the helpful information you provide in your articles
BaddieHub I’m often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your web site and maintain checking for brand spanking new information.
I’m really glad to hear that my article helped you feel hopeful!
I have been browsing online more than three hours today yet I never found any interesting article like yours It is pretty worth enough for me In my view if all website owners and bloggers made good content as you did the internet will be a lot more useful than ever before
I’m really glad to hear that my article helped you feel hopeful!
I do not even know how I ended up here but I thought this post was great I do not know who you are but certainly youre going to a famous blogger if you are not already Cheers
I’m really glad to hear that my article helped you feel hopeful!
Nutra Gears For the reason that the admin of this site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents.
I’m really glad to hear that my article helped you feel hopeful!
Your blog is a true hidden gem on the internet. Your thoughtful analysis and engaging writing style set you apart from the crowd. Keep up the excellent work!
I’m really glad to hear that my article helped you feel hopeful!
Henof There is definately a lot to find out about this subject. I like all the points you made
I’m really glad to hear that my article helped you feel hopeful!
helloI really like your writing so a lot share we keep up a correspondence extra approximately your post on AOL I need an expert in this house to unravel my problem May be that is you Taking a look ahead to see you
Thank you for your feedback! I’m glad you enjoyed the content and found it engaging.